(Created page with "The development of biological devices that transform living cells into biosensors, nano-factories, and therapeutic agents is the objective of synthetic biology. CeCyL is a un...") |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<mediaplayer width='550' height='300'>http://www.ccy.zcu.cz/movies/DEP_Focusing.mov</mediaplayer> | <mediaplayer width='550' height='300'>http://www.ccy.zcu.cz/movies/DEP_Focusing.mov</mediaplayer> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:37, 3 January 2015
The development of biological devices that transform living cells into biosensors, nano-factories, and therapeutic agents is the objective of synthetic biology. CeCyL is a university wide research laboratory interested in innovations that make such devices reliable and efficient enough to make the biological systems a generally useful technology. We apply tools from engineering and synthetic biology to 1) build electromechanical devices co-designed with biological devices, 2) derive estimation and modeling methods specifically for biological systems, and 3) develop biological control mechanisms and theory.
If you are interested in joining us in this effort or if you are just simply interested, contact Dr. Daniel Georgiev (georgiev@kky.zcu.cz).
Contents
Experimental Design
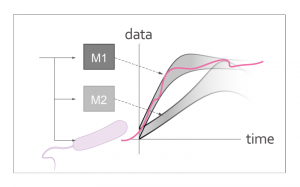
Systems biologists are often faced with competing models for a given experimental system. Performing experiments can be time-consuming and expensive. Therefore, a method for designing experiments that, with high probability, discriminate between competing models is desired. Model discrimination of biochemical models unfortunately poses a computationally difficult problem. CeCyL is interested in solving this problem for special cases that are important in experimental design. The solutions yield informative experimental inputs. The solutions also guide the biological design to ensure that it can later be reliably modeled and predicted.
Gene Tuning
Transcription networks are commonly used in synthetic biology to implement a wide variety of regulatory, logic, and temporal functions. Tuning of transcription networks is commonly achieved by design of the gene promoter regions. Characterized promoter libraries serve well in this design as an initial starting point (Hammer 2006). As with any engineered system, however, precise behavior is attained by in vivo fine tuning. Model based tuning is made difficult by inherent biological model overparametrization (Gutenkunst 2008). Tuning using high throughput assays is also prohibitive both in terms of experimental workload and precision. CeCyL is working on developing precise model-free tuning protocols. These are protocols that are able to identify small differences between competing promoter designs and isolate the ones that yield desirable behaviors, e.g., robustness to common perturbations, fast activation times, sufficient temporal spacings, and correct equilibrium concentrations.
Electricity Generation
All cells produce in their membranes electric currents that do work, e.g., ATP synthesis or flagellar movement. Many of these electric currents depend on the presence of oxygen in the extracellular environment. If the oxygenated medium is separated from microbial populations by an electron conductor (such as a mixed carbon/metallic circuit), then certain types of microbes can continue to utilize oxygen via the conductor to maintain their membrane electric activity. In return, electricity is produced. CeCyL is interested in developing this technology (i.e., to make it more efficient and stable) using genetic devices that improve the organisms electrogenic and oxidative characteristics.
Division Control
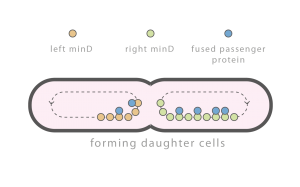
Individual cells are constantly subject to perturbations: exogenous perturbations such as temperature fluctuations, brownian motion related perturbations, and perturbations caused by cell division. Cell division related perturbations are primarily caused by random partitioning of molecules between daughter cells and can be difficult to attenuate. Important molecules, e.g., chromosomes, implement complex mechanisms to ensure equal partitioning. Other molecules, e.g., the majority of proteins, are simply partitioned at random. CeCyL is interested in developing simple mechanisms to regulate general protein partitioning.
Time lapse of E. coli with an integrated Min D::GFP fusion protein. Observed spatial-temporal oscillations are critical for correct cell division.
The media player is loading...
Cell Sorting
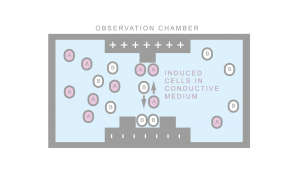
Numerous methods of cell separation exist. Primitive methods ignore cellular composition (size based separation). Expensive methods utilize fluorescent markers together with expensive laser sorters (FACS). Other methods require exogenous labels and known protein interactions (magneto-phoresis). Such interactions can be non-specific. Hence, only sufficiently disparate phenotypes can be isolated. Dielectrophoretic separation is based on forces generated directly by the cellular makeup. Hence multiplexed separation and multilevel separation is possible. Programmed cells can also be used as probes for logic enabled labeling. CeCyL in collaboration with FEL UWB is interested in developing dielectrophoretic separation methods together with compatible biological devices.
Dielectrophoretic cell focusing microfluidic device developed at CeCyL. The presence of an electric field tuned to a specific frequency allows the cells to be focused by negative dielectric forces to the center of the channel.
The media player is loading...